When residual gas analysis is performed in ultra-high vacuum/extreme-high vacuum (UHV/XHV) at 10-7 Pa (10-9 mbar) or lower using a typical quadrupole residual gas analyzer, the out gas from the ion sources at the sensor tips can no longer be ignored, and it becomes extremely difficult to perform high-precision gas analysis.
WATMASS is a product where the ion source has been improved to allow high precision residual gas analysis in the lower 10-7 Pa (10-9 mbar) range.
Ultra low out gassing QMS
- Excellent performance in XHV/UHV application
- Ultra-Low Outgassing from an Ion Source
- Modified Ion source with 0.2% BeCu alloy
- Pt-Ir alloy Grid with High Power Degas
- NiP treatment on Copper surface (out side)
- 0.2% BeCu alloy Nipple tube (145mm)
- No welding for BeCu material
- Significant reduction for H2 and ESD noise (ESD: Electron Stimulated Desorption)

Ion Source

Specifications
| Mass Range | 100, 200, 300 amu |
|---|---|
| Detector Type | FC/EM |
| Ion Energy | 70eV |
| Filament | Y2O3Ir, Dual |
| Sensitivity | 1.0 x 10-6 A/Pa (100amu FC Sensor) |
| Measurement Speed | 1.8 msec (Min.) |
| Sensor Operating Temp. | 200°C (FC), 150°C (EM) |
| Max. Bakeout Temp. | 300°C (Electronics removed) |
| Network | TCP/IP ethernet connectivity |
| Software | FabGuard Explore (Windows 7, 8.1, 10) |
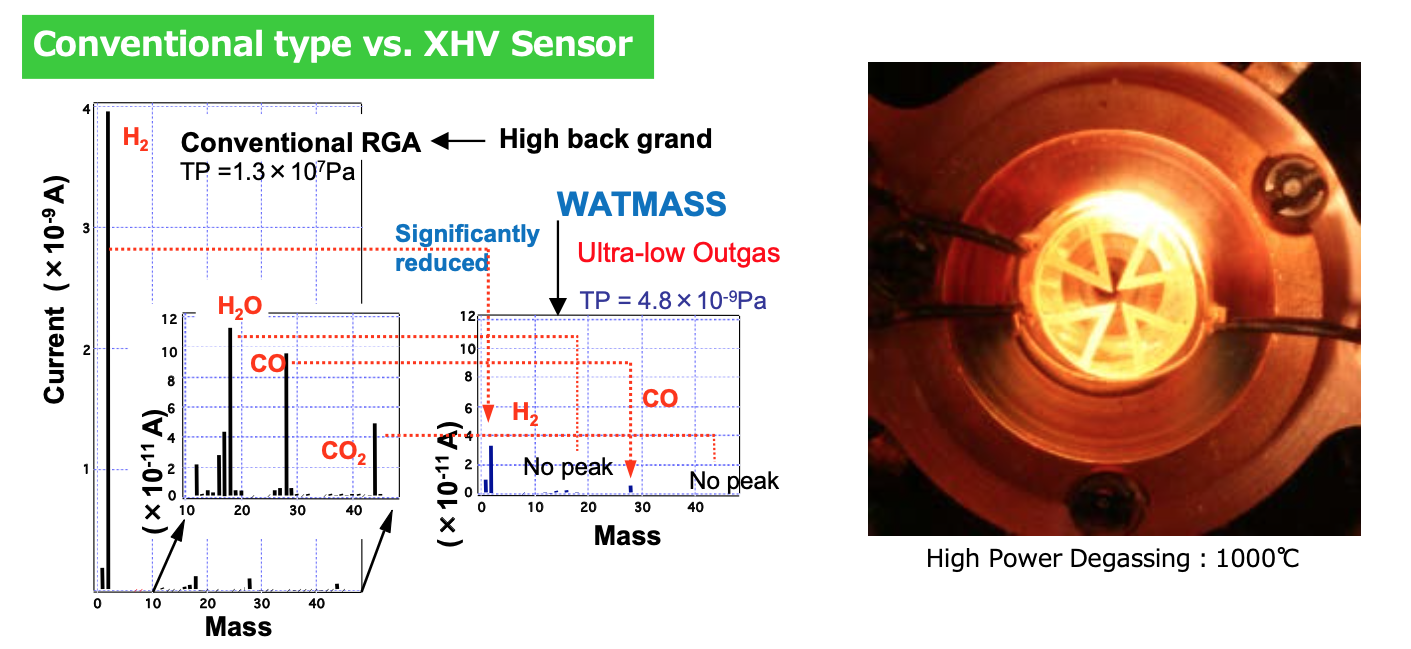
Key points of WATMASS for greatly reducing out gas
- By adopting 0.2% BeCu material with low radiation/high conduction for the hot cathode ion source
- and sensor nipple (DN40CF), energy savings are achieved and the ion source temperature is lowered,
- which greatly reduces low out gases.
- ESD noise are reduced by fabricating the grid from platinum-iridium (Pt-Ir) alloy.
(combined use for high power and electron bombardment) - Hydrogen is emitted and a Be oxide layer is formed by thorough degassing using an electric furnace
Example Applications
- XHV/UHV high precision gas analysis
- Surface analysis
- Degradation of and gas emission from semiconductor devices
- Analysis of gas emitted by optical stimulation or electrical stimulation
- Trace gas analysis (TDS/Out Gas)
- Sealed device/MEMS gas analysis for leak and distractive testing at the 10-16 Pa⋅m3/s (He) level
- He transmission testing of glass and microbubble gas analysis
Principle of low outgas
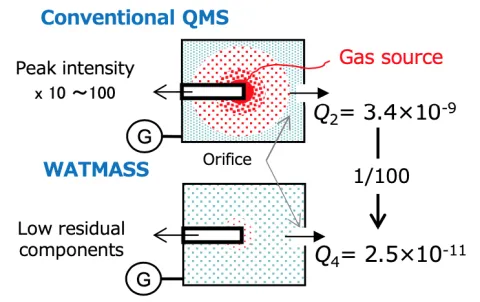
Q2 and Q4 in the diagram are the out gas volumes from the sensor as found by the orifice method. Since the gas source before improvement is from the hot filament at the sensor tip, the gas pressure is locally high.
When the residual gas is analyzed in this high (local pressure) state, the obtained strength is also 10 to 100 times higher, and the gas peak is 1000 to 10000 times larger than the true value. In contrast, in the sensor after low out gas improvement, true gas analysis is possible since the amount of out gas is around 2 times higher than when the hot filament is on.
Measurement result of outgas
| Conditions | Conventional QMS | Watmass | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filament - off | Base Pressure | P = 2.4 x 10-7 Pa | P = 2.8 x 10-8 Pa |
| Outgas | Q1 = 2.3 x 10-10 Pa*m3/s | Q3 = 1.4 x 10-11 Pa*m3/s | |
| Filament - on | Base Pressure | P = 3.5 x 10-6 Pa | P = 2.5 x 10-8 Pa |
| Outgas | Q2 = 3.4 x 10-9 Pa*m3/s | Q4 = 2.5 x 10-11 Pa*m3/s | |
| |||